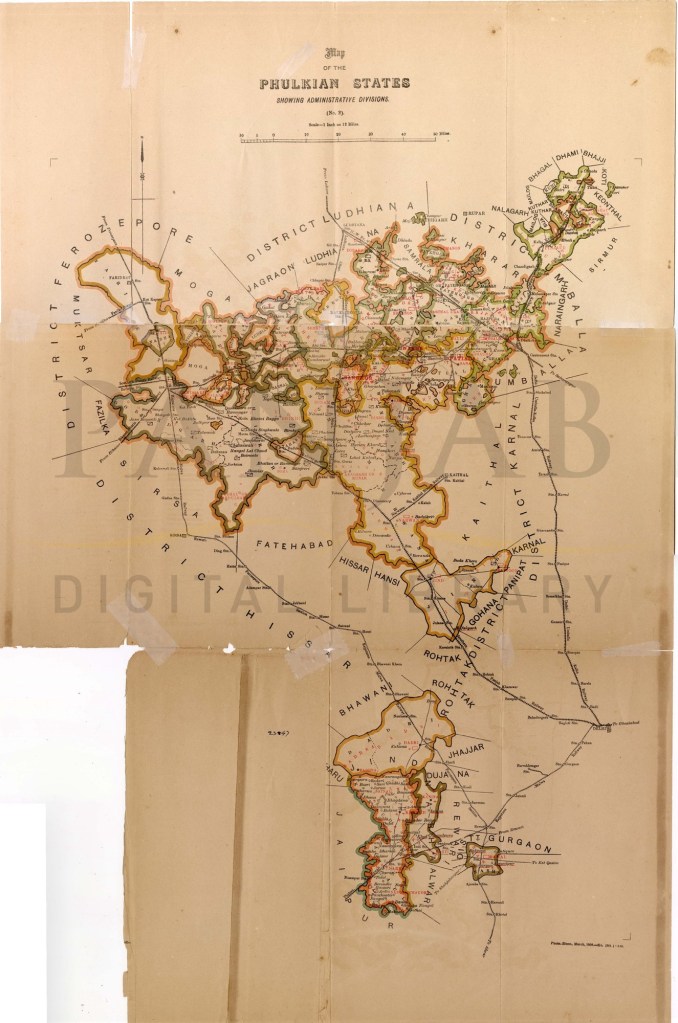
ਫੁਲਕੀਆਂ ਰਿਆਸਤਾਂ – ਇਤਿਹਾਸਕ ਪਿਛੋਕੜ
ਫੁਲਕੀਆਂ ਮਿਸਲ
ਫੁਲਕੀਆਂ ਮਿਸਲ ਅਠਾਰਵੀਂ ਸਦੀ ਦਾ ਇਕ ਸਿੱਖ ਰਾਜਸੀ ਗੋਤ ਹੈ, ਜੋ ਦਰਿਆ ਸਤਲੁਜ ਦੇ ਦੱਖਣੀ ਖੇਤਰ ਵਿੱਚ ਉੱਤੇ ਉੱਥਾਰਿਆ ਸੀ। ਇਹ ਮਿਸਲ ਦੂਜੀ ਮਿਸਲ ਵਜੋਂ ਜਾਣੀ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਸੀ, ਹਾਲਾਂਕਿ ਇਹ ਦੂਜੇ ਗਿਆਰਾਂ ਮਿਸਲਾਂ ਦੀ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਦਲ ਖ਼ਾਲਸਾ ਵਿੱਚ ਸ਼ਾਮਿਲ ਨਹੀਂ ਸੀ।ਕਿਉਂਕਿ ਇਹ ਰਾਜਨੀਤਿਕ ਤੌਰ ’ਤੇ ਅਕਸਰ ਮੁਗਲਾਂ ਜਾਂ ਬਾਅਦ ਵਿੱਚ ਬ੍ਰਿਟਿਸ਼ ਹਕੂਮਤ ਨਾਲ ਸੰਝੌਤਾ ਕਰ ਲੈਂਦੇ ਸਨ।
ਪਰ ਕੁਝ ਇਤਿਹਾਸਕਾਰ ਮੰਨਦੇ ਹਨ ਕਿ ਫੁਲਕੀਅਨ ਸ਼ਾਸਕ, ਭਾਵੇਂ ਮੁੱਖ ਰੂਪ ਵਿੱਚ ਨਹੀਂ, ਪਰ ਕਈ ਵਾਰ ਸਿਆਸੀ/ਫੌਜੀ ਤੌਰ ’ਤੇ ਦਲ ਖ਼ਾਲਸਾ ਨਾਲ ਸਹਿਯੋਗ ਕਰਦੇ ਰਹੇ।
1809 ਵਿਚ ਤਿੰਨੇ ਰਾਜਾਂ ਨੇ ਬ੍ਰਿਟਿਸ਼ ਈਸਟ ਇੰਡੀਆ ਕੰਪਨੀ ਨਾਲ ਸਾਂਝੇ ਤੌਰ ’ਤੇ ਸੁਰੱਖਿਆ ਸੰਧੀ ਕੀਤੀ, ਜਿਸ ਨਾਲ ਇਹ ਰਾਜ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਰਣਜੀਤ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੀ ਵਧਦੀ ਹੋਈ ਲਹਿਰ ਤੋਂ ਬਚ ਗਏ। ਇਸ ਸੰਧੀ ਦੇ ਬਾਅਦ ਇਹ ਰਾਜਾਂ ਆਪਣੇ ਅਲੱਗ ਰਾਜਸੀ ਰੂਪ ’ਚ ਕਾਇਮ ਰਹੇ, ਪਰ ਉਹ ਸਿੱਖ ਇਕਜੁੱਟਤਾ ਤੋਂ ਵੱਖਰੇ ਰਹਿ ਗਏ।
ਫੁਲਕੀਅਨ ਮਿਸਲ ਨੇ ਸਿਰਫ ਰਾਜਨੀਤਿਕ ਪੱਖੋਂ ਹੀ ਨਹੀਂ, ਸਗੋਂ ਸਿੱਖ ਸੰਸਕ੍ਰਿਤੀ, ਸੰਗੀਤ, ਵਿਰਾਸਤ ਅਤੇ ਸ਼ਿਲਪਕਲਾ ਵਿੱਚ ਵੀ ਯੋਗਦਾਨ ਪਾਇਆ। ਪਟਿਆਲਾ ਘਰਾਣਾ ਸੰਗੀਤ, ਮਹਿਲਾਂ, ਕਿਲਿਆਂ ਅਤੇ ਗ੍ਰੰਥਾਂ ਦੇ ਰੂਪ ਵਿੱਚ ਇਹ ਵਿਰਾਸਤ ਅੱਜ ਵੀ ਜਿਊਂਦੀ ਹੈ।
Here is a clean, structured Phulkian Misl summary table for your website, in both Punjabi and English. You can directly paste this into your WordPress editor using a table block or shortcode plugin.
📋 Phulkian Misl
| ਮੁੱਖ ਜਾਣਕਾਰੀ | Details (English) | ਵੇਰਵਾ (Punjabi) |
|---|---|---|
| ਸਥਾਪਕ | Phul (d. 1652), Sidhu-Brar Jatt | ਫੂਲ (ਮੌਤ 1652), ਸਿੱਧੂ-ਬਰਾਰ ਜੱਟ |
| ਪਿੰਡ/ਮੂਲ ਥਾਂ | Phul Village, Bathinda District | ਪਿੰਡ ਫੂਲ, ਬਠਿੰਡਾ ਜ਼ਿਲ੍ਹਾ |
| ਗੁਰੂ ਸਬੰਧ | Blessed by Guru Har Rai Ji & Guru Gobind Singh Ji | ਗੁਰੂ ਹਰ ਰਾਇ ਜੀ ਅਤੇ ਗੁਰੂ ਗੋਬਿੰਦ ਸਿੰਘ ਜੀ ਦੀ ਕਿਰਪਾ |
| ਵਿਖਿਆਤ ਉਕਤੀ | “Tera Ghar Mera Asay” | “ਤੇਰਾ ਘਰ ਮੇਰਾ ਅਸੈ” |
| ਮੁੱਖ ਰਾਜ | Patiala, Nabha, Jind | ਪਟਿਆਲਾ, ਨਾਭਾ, ਜੀਂਦ |
| ਰਾਜਸੀ ਸੰਧੀ (British) | 1809 – Treaty of Protection with East India Company | 1809 – ਬ੍ਰਿਟਿਸ਼ ਨਾਲ ਸੁਰੱਖਿਆ ਸੰਧੀ |
| ਮੁਕਾਬਲਤੀ ਸਿੱਖ ਰਾਜਨੀਤੀ | Remained separate from Maharaja Ranjit Singh’s Empire | ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਰਣਜੀਤ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੀ ਸਿੱਖ ਰਾਜ ਨੀਤੀ ਤੋਂ ਵੱਖਰੇ ਰਹੇ |
| ਸੰਸਕ੍ਰਿਤਿਕ ਯੋਗਦਾਨ | Music (Patiala Gharana), Architecture, Education | ਸੰਗੀਤ (ਪਟਿਆਲਾ ਘਰਾਣਾ), ਇਮਾਰਤਾਂ, ਸਿੱਖਿਆ |
| ਵਿਰਾਸਤ ਰਾਜਾਂ ਦੇ ਉਤਸ਼ਾਹੀ ਸ਼ਾਸਕ | Amar Singh, Bhupinder Singh, Heera Singh etc. | ਅਮਰ ਸਿੰਘ, ਭੁਪਿੰਦਰ ਸਿੰਘ, ਹੀਰਾ ਸਿੰਘ ਆਦਿ |
| ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਵਿਲੀਨਤਾ | Joined Indian Union in 1947–48 | 1947–48 ਵਿੱਚ ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਹੋਏ |
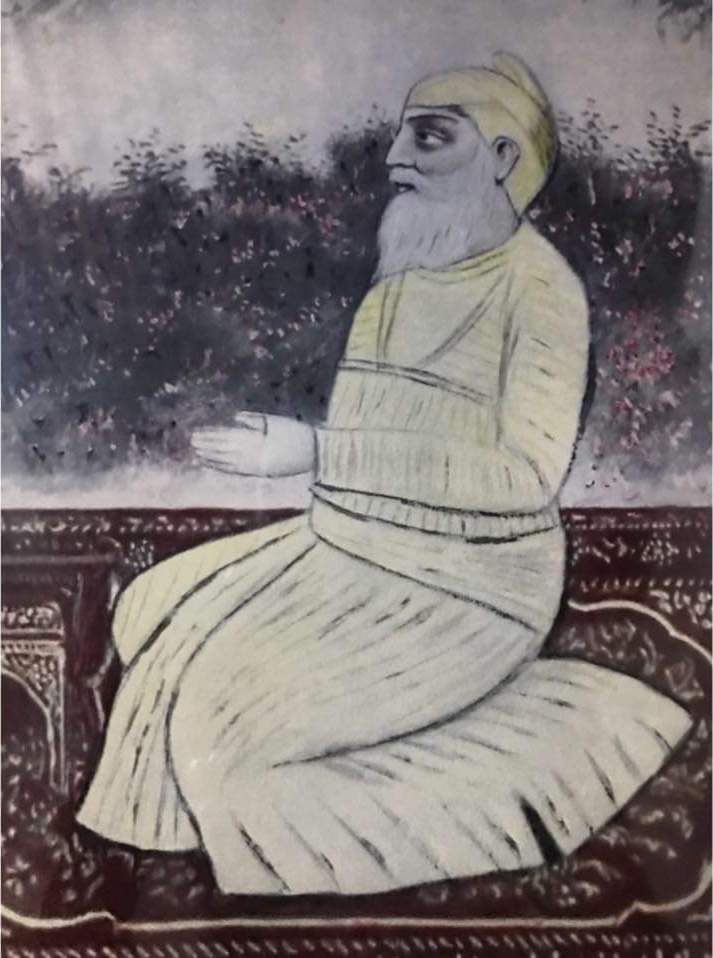

ਇਸ ਰਾਜਸੀ ਰੂਟ ਦੀ ਸ਼ੁਰੂਆਤ ਫੂਲ (ਮੌਤ 1652) ਤੋਂ ਹੋਈ, ਜੋ ਇੱਕ ਸਿੱਧੂ ਜੱਟ ਸੀ ਅਤੇ ਫੂਲ ਪਿੰਡ (ਹੁਣ ਬਠਿੰਡਾ ਜ਼ਿਲ੍ਹਾ, ਪੰਜਾਬ) ਦਾ ਨਿਵਾਸੀ ਸੀ। ਉਹ ਆਪਣੇ ਯਾਤਰਾ ਦੌਰਾਨ ਗੁਰੂ ਹਰ ਰਾਇ ਜੀ ਨੂੰ ਮਿਲੇ ਅਤੇ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਤੋਂ ਅਸ਼ੀਰਵਾਦ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਕੀਤਾ। ਫੂਲ ਦੇ ਘਰ ਨੂੰ ਗੁਰੂ ਗੋਬਿੰਦ ਸਿੰਘ ਜੀ ਨੇ ਵੀ ਅਸ਼ੀਰਵਾਦ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਅਤੇ ਇੱਕ ਹੁਕਮਨਾਮਾ ਜਾਰੀ ਕੀਤਾ ਜਿਸ ਵਿੱਚ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੇ ਫੂਲ ਦੇ ਵੰਸ਼ਜਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਸੈਨਿਕ ਸਹਾਇਤਾ ਲਈ ਕਿਹਾ ਅਤੇ ਕਿਹਾ “ਤੇਰਾ ਘਰ ਮੇਰਾ ਅਸੈ”
The Punjab Past and Present” ਵਿੱਚ ਫੂਲ ਦੀ ਕਥਾ, ਗੁਰੂ ਹਰ ਰਾਇ ਜੀ ਅਤੇ ਗੁਰੂ ਗੋਬਿੰਦ ਸਿੰਘ ਜੀ ਦੇ ਅਸ਼ੀਰਵਾਦ ਦੀ ਗੱਲ ਆਉਂਦੀ ਹੈ। ਇਹ ਪੁਸ਼ਟੀ ਕਰਦੀ ਹੈ ਕਿ ਜੋ ਲਿਖਿਆ — “ਤੇਰਾ ਘਰ ਮੇਰਾ ਅਸੈ” — ਇਹ ਗੁਰੂ ਸਾਹਿਬ ਦੀ ਕਥਾ ਤੋਂ ਆਧਾਰਿਤ ਹੈ।
🔹 ਤਥਾਂਕਤ ਸਬੂਤ:
• “ਫੁਲਕੀਅਨ” ਨਾਂ ਫੂਲ ਪੁਰਖ ਅਤੇ ਉਸ ਪਿੰਡ ਤੋਂ ਹੀ ਆਇਆ ਹੈ।
• “The Punjab Past and Present” ਅਤੇ 1961 ਦੀ ਸੰਗਰੂਰ ਜ਼ਿਲ੍ਹਾ ਦੀ ਗਣਨਾ ਰਿਪੋਰਟ (Census Handbook) ਵਿੱਚ ਇਹ ਪੁਸ਼ਟੀ ਕੀਤੀ ਗਈ ਹੈ ਕਿ ਫੂਲ ਦੇ ਪੁੱਤਰਾਂ (ਤਿਲੋਕ ਸਿੰਘ, ਰਾਮ ਸਿੰਘ ਆਦਿ) ਨੇ ਨਾਭਾ, ਜੀਂਦ, ਅਤੇ ਪਟਿਆਲਾ ਰਾਜਿਆਂ ਦੀ ਨੀਂਹ ਰੱਖੀ।

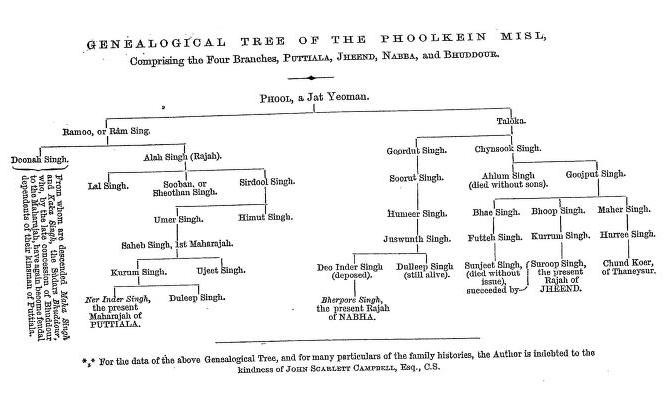
ਫੂਲ ਦੇ ਸੱਤ ਪੁੱਤਰ ਸਨ। ਉਸ ਦੇ ਵੱਡੇ ਪੁੱਤਰ ਤਿਲੋਕ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੇ ਨਾਭਾ ਅਤੇ ਜੀਂਦ ਦੇ ਰਾਜਸੀ ਰਾਜਾਂ ਦੀ ਸਥਾਪਨਾ ਕੀਤੀ, ਜਦੋਂ ਕਿ ਦੂਜੇ ਪੁੱਤਰ ਰਾਮ ਸਿੰਘ ਪਟਿਆਲਾ ਦੇ ਰਾਜਿਆਂ ਦੇ ਪੂਰਵਜ ਬਣੇ।
ਫੂਲ ਦੇ ਵੰਸ਼ਾਂ ਨੇ ਸਿੱਖ ਫੌਜੀ ਮੁਹਿੰਮਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਮੁੱਖ ਭੂਮਿਕਾ ਅਦਾ ਕੀਤੀ ਅਤੇ ਬੰਦਾ ਸਿੰਘ ਬਹਾਦਰ ਦੀ ਮਦਦ ਕੀਤੀ, ਜੋ ਮੁਗਲ ਦਬਦਬੇ ਖਿਲਾਫ ਲੜ ਰਿਹਾ ਸੀ।
ਬਾਬਾ ਆਲਾ ਸਿੰਘ ਅਤੇ ਪਟਿਆਲਾ ਦੀ ਸਥਾਪਨਾ
ਇਸ ਵਿਚਾਰਧਾਰਾ ਦੇ ਪ੍ਰਮੁੱਖ ਵੰਸ਼ਜ ਬਾਬਾ ਆਲਾ ਸਿੰਘ ਸਨ, ਜੋ ਰਾਮ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੇ ਪੁੱਤਰ ਸਨ ਅਤੇ ਇੱਕ ਬਹਾਦਰ ਸਿਪਾਹੀ ਅਤੇ ਚਤੁਰ ਰਾਜਨੀਤੀਕਾਰ ਸੀ।
1732 ਤੱਕ ਉਹ ਬਰਨਾਲਾ ਦੇ ਆਲੇ-ਦੁਆਲੇ ਇੱਕ ਵਿਸ਼ਾਲ ਖੇਤਰ ਜਿੱਤ ਚੁੱਕੇ ਸਨ, ਜੋ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦਾ ਮੁੱਖ ਦਫਤਰ ਬਣ ਗਿਆ ਸੀ। 1740 ਅਤੇ 1750 ਦੀਆਂ ਦਹਾਕਿਆਂ ਵਿੱਚ, ਦੁਰਾਨੀ ਅਤੇ ਮੁਗਲ ਟੱਕਰਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਪਟਿਆਲਾ ਦਾ ਰਾਜ ਤੱਕ ਸ਼ਾਮਿਲ ਹੋ ਗਏ ਅਤੇ ਬਾਬਾ ਆਲਾ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੇ ਸਰਹਿੰਦ ਦੇ ਖੇਤਰਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਜਿੱਤਿਆ ਅਤੇ ਸੁਨਾਮ, ਸਮਾਣਾ, ਸਨੌਰ ਅਤੇ ਟੋਹਾਣਾ ਜਿਹੇ ਮਹੱਤਵਪੂਰਨ ਸ਼ਹਿਰਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਕਬਜ਼ਾ ਕੀਤਾ।
ਬਾਬਾ ਆਲਾ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੀ ਲੀਡਰਸ਼ਿਪ, ਬਰਨਾਲਾ ਤੋਂ ਪਟਿਆਲਾ ਸ਼ਹਿਰ ਦੀ ਸਥਾਪਨਾ ਅਤੇ ਅਮਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੀ ਪੂਰਵਜੀ ਗੱਲ ਕੀਤੀ ਹੈ, ਇਹ Census Handbook (Sangrur) ਅਤੇ Ganda Singh ਦੀ ਲਿਖਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਪੂਰੀ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੱਸਿਆ ਗਿਆ ਹੈ।

1753 ਵਿੱਚ, ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੇ ਬਰਨਾਲਾ ਤੋਂ 100 ਕਿਲੋਮੀਟਰ ਪੂਰਬ ਇੱਕ ਕਿਲਾ ਬਣਾਉਣਾ ਸ਼ੁਰੂ ਕੀਤਾ। ਇਸ ਕਿਲੇ ਦੇ ਆਲੇ-ਦੁਆਲੇ ਪਟਿਆਲਾ ਸ਼ਹਿਰ ਵਧਿਆ (ਪੱਟੀ = ਵਾਰਡ, ਆਲਾ = ਆਲਾ ਸਿੰਘ ਦਾ) ਅਤੇ 1763 ਵਿੱਚ ਪਟਿਆਲਾ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੀ ਰਾਜਧਾਨੀ ਬਣ ਗਈ।
ਬਾਬਾ ਆਲਾ ਸਿੰਘ 1765 ਵਿੱਚ ਅਗਸਤ ਮਹੀਨੇ ਵਿੱਚ ਦੁਨੀਆਂ ਤੋਂ ਵਿਦਾ ਹੋ ਗਏ। ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੇ ਪੋਤੇ, ਅਮਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੇ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੀ ਥਾਂ ਲਈ ਅਤੇ ਅਹਿਮਦ ਸ਼ਾਹ ਅਬਦਾਲੀ ਤੋਂ ਰਾਜਾ-ਏ-ਰਾਜਗਨ ਦਾ ਖਿਤਾਬ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਕੀਤਾ, ਕਿਉਂਕਿ ਅਮਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੇ ਅਬਦਾਲੀ ਦੀ ਮਦਦ ਕੀਤੀ ਸੀ।
ਅਮਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੇ ਪਟਿਆਲਾ ਦੇ ਖੇਤਰ ਨੂੰ ਕਾਫੀ ਵਧਾਇਆ ਅਤੇ ਬਠਿੰਡਾ, ਮਾਨਸਾ, ਕੋਟਕਪੂਰਾ, ਸੈਫਾਬਾਦ ਅਤੇ ਪਿੰਜੌਰ ਨੂੰ ਆਪਣੇ ਕਬਜ਼ੇ ਵਿੱਚ ਲਿਆ। ਇਹ ਸਾਰੇ ਖੇਤਰ ਉਹਨਾਂ ਨੇ ਜ਼ਿਆਦਾਤਰ ਗੈਰ-ਸਿੱਖ ਰਾਜਿਆਂ ਨਾਲ ਗਠਜੋੜ ਕਰਕੇ ਜਿੱਤਣ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਫਲ ਹੋਏ।
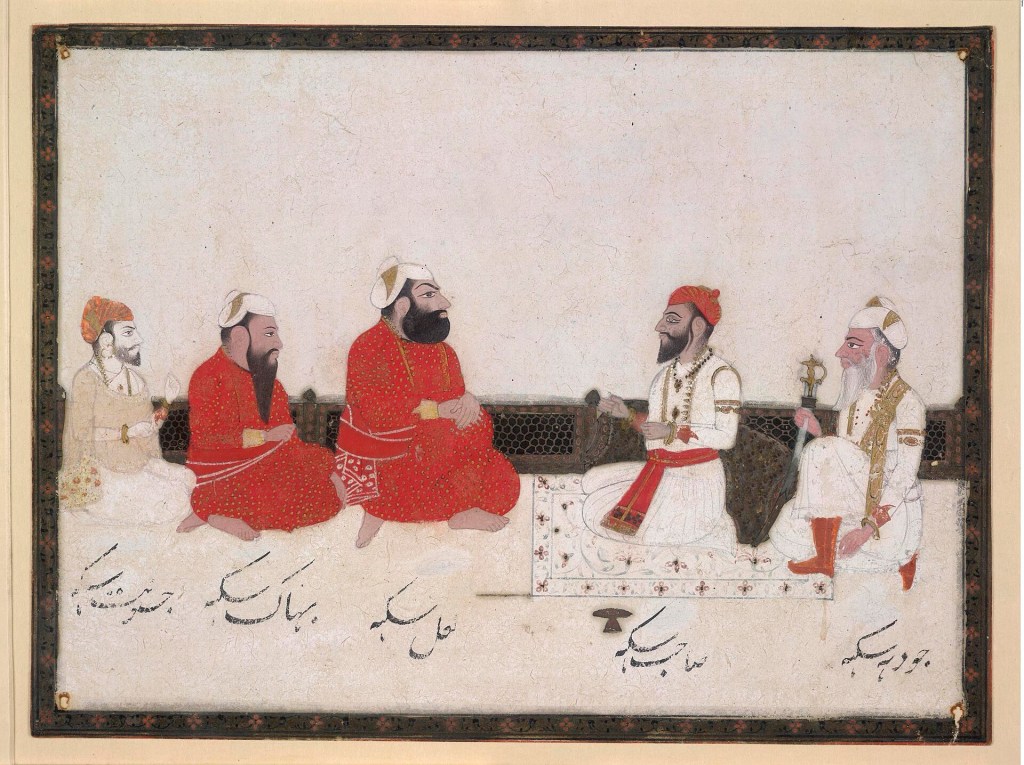

ਬ੍ਰਿਟਿਸ਼ ਰੱਖਿਆ ਅਧੀਨ
ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਅਮਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੇ ਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ, ਪਟਿਆਲਾ ਯਮੁਨਾ ਅਤੇ ਸਤਲੁਜ ਦਰਿਆਵਾਂ ਵਿਚਕਾਰ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਸ਼ਕਤੀਸ਼ਾਲੀ ਸਿੱਖ ਰਾਜ ਬਣ ਗਿਆ।
1809 ਵਿੱਚ, ਉਹਨਾਂ ਦੇ ਪਿੱਛੇ ਆਉਣ ਵਾਲੇ ਬੱਚੇ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਸਾਹਿਬ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੇ ਗੈਰ-ਸਿੱਖ ਰਾਜਿਆਂ ਨਾਲ ਮਿਲਕੇ ਬ੍ਰਿਟਿਸ਼ ਰੱਖਿਆ ਅਧੀਨ ਹੋਣ ਦਾ ਫੈਸਲਾ ਕੀਤਾ।
ਪਟਿਆਲਾ ਦੇ ਸਿੱਖ ਰਾਜ ਦੇ ਸਿਖਰ ਵਾਲੇ ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ:
• ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਕਰਮ ਸਿੰਘ (1813-1845)
• ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਨਰਿੰਦਰ ਸਿੰਘ (1845-1862)
• ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਮਹਿੰਦਰ ਸਿੰਘ (1862-1876)
• ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਰਾਜਿੰਦਰ ਸਿੰਘ (1876-1900)
• ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਭੁਪਿੰਦਰ ਸਿੰਘ (1900-1938)
• ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਸਰ ਯਾਦਵਿੰਦਰ ਸਿੰਘ, ਜਿਸਨੇ 1947 ਵਿੱਚ ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਕਰਨ ਲਈ ਆਗਿਆ ਪੱਤਰ ਤੇ ਸਾਈਨ ਕੀਤੇ। ਪਟਿਆਲਾ ਨੂੰ 1948 ਵਿੱਚ ਪਟਿਆਲਾ ਅਤੇ ਪੂਰਬੀ ਪੰਜਾਬ ਸੂਬਾ ਯੂਨੀਅਨ ਵਿੱਚ ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ।

ਨਾਭਾ ਰਾਜ
ਫੁਲਕੀਅਨ ਮਿਸਲ ਦੇ ਨਾਭਾ ਸ਼ਾਖਾ ਦੀ ਸਥਾਪਨਾ ਹਮੀਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੇ ਕੀਤੀ, ਜੋ ਫੂਲ ਦੇ ਪੁੱਤਰ ਤਿਲੋਕ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੇ ਵੰਸ਼ਜ ਸਨ। 1755 ਵਿੱਚ, ਹਮੀਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੇ ਨਾਭਾ ਸ਼ਹਿਰ ਦੀ ਸਥਾਪਨਾ ਕੀਤੀ।
1764 ਵਿੱਚ, ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੇ ਬਾਬਾ ਆਲਾ ਸਿੰਘ, ਸਰਦਾਰ ਨਾਨੂ ਸਿੰਘ ਸੈਣੀ ਅਤੇ ਦਲ ਖ਼ਾਲਸਾ ਨਾਲ ਮਿਲ ਕੇ ਸਰਹਿੰਦ ਦੀ ਜੰਗ ਵਿੱਚ ਭਾਗ ਲਿਆ ਅਤੇ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਅਮਲੋਹ ਦੀ ਪਰਗਣਾ ਵਾਰਸ ਵਜੋਂ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਹੋਈ।
ਹਮੀਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੇ ਆਪਣੇ ਆਪ ਨੂੰ ਆਜ਼ਾਦ ਐਲਾਨ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਅਤੇ ਆਪਣੇ ਰਾਜ ਵਿੱਚ ਪੈਸਾ ਛਪਵਾਣ ਦਾ ਅਧਿਕਾਰ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਕੀਤਾ। 1783 ਵਿੱਚ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੀ ਮੌਤ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਅਦ, ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੇ ਪੁੱਤਰ ਜਸਵੰਤ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੇ ਰਾਜ ਦੀ ਕੁੱਲ ਸਥਿਤੀ ਨੂੰ ਸੰਭਾਲਿਆ ਅਤੇ ਪਹਿਲਾਂ ਜੀਂਦ ਅਤੇ ਫਿਰ ਪਟਿਆਲਾ ਖਿਲਾਫ ਲੰਬੀ ਜੰਗ ਲੜੀ।
ਜਸਵੰਤ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੂੰ ਬ੍ਰਿਟਿਸ਼ ਰੱਖਿਆ ਵੀ ਮਿਲਿਆ 1809 ਵਿੱਚ।
ਨਾਭਾ ਰਾਜ ਦੇ ਸ਼ਾਸਕ:
• ਰਾਜਾ ਦੇਵਿੰਦਰ ਸਿੰਘ (1840–1846)
• ਰਾਜਾ ਭਰਪੂਰ ਸਿੰਘ (1847–1863)
• ਰਾਜਾ ਭਗਵਾਨ ਸਿੰਘ (1866–1871)
• ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਹੀਰਾ ਸਿੰਘ (1871–1911)
• ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਰਿਪੁਦਾਮਨ ਸਿੰਘ (1911–1923), 1923 ਵਿੱਚ ਹਟਾਇਆ ਗਿਆ।
• ਮਹਾਰਾਜਾ ਪ੍ਰਤਾਪ ਸਿੰਘ, ਜਿਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੇ ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਹੋਣ ਲਈ ਆਗਿਆ ਪੱਤਰ ’ਤੇ ਸਾਈਨ ਕੀਤੇ।
ਇਹ ਗੱਲ ਵੀ “Punjab Past & Present” ਅਤੇ Census 1961 Sangrur Handbook ਵਿੱਚ ਮਿਲਦੀ ਹੈ — ਨਾਭਾ ਰਾਜ ਦੀ ਸ਼ੁਰੂਆਤ ਹਮੀਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੇ ਕੀਤੀ, ਸਰਹਿੰਦ ਦੀ ਜੰਗ ਵਿੱਚ ਹਿੱਸਾ ਲਿਆ, ਅਤੇ ਅਮਲੋਹ ਪਰਗਣੇ ਦੀ ਮਲਕੀਅਤ ਮਿਲੀ।

ਜੀਂਦ ਰਾਜ
ਫੁਲਕੀਅਨ ਮਿਸਲ ਦਾ ਤੀਸਰਾ ਰਾਜ, ਜੀਂਦ, ਗਜਪਤ ਸਿੰਘ (1738–1789) ਦੁਆਰਾ ਸਥਾਪਤ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ ਸੀ, ਜੋ ਸੁਖਚੈਨ ਸਿੰਘ ਦੇ ਪੁੱਤਰ ਸਨ।
1764 ਵਿੱਚ, ਗਜਪਤ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੇ ਜੱਸਾ ਸਿੰਘ ਆਹੁਵਾਲੀਆ ਦੇ ਨੈਤ੍ਰਿਤਵ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਰਹਿੰਦ ਨੂੰ ਜਿੱਤਣ ਲਈ ਲੜਾਈ ਵਿੱਚ ਭਾਗ ਲਿਆ ਅਤੇ ਜੀਂਦ, ਸਫੀਦੋਂ, ਅਤੇ ਪਾਨੀਪਤ ਅਤੇ ਕਰਨਾਲ ਦੇ ਖੇਤਰਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਕਬਜ਼ਾ ਕੀਤਾ।
1766 ਵਿੱਚ, ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੇ ਜੀਂਦ ਨੂੰ ਆਪਣੀ ਰਾਜਧਾਨੀ ਬਣਾਈ। ਗਜਪਤ ਸਿੰਘ ਨੇ ਬਹੁਤ ਸਿੱਖ ਰਾਜਿਆਂ ਤੋਂ ਵੱਖਰਾ, ਮੁਗਲ ਸਮਰਾਟ ਦੀ ਆਧਿਕਾਰਤਾ ਨੂੰ ਕਬੂਲ ਕੀਤਾ, ਹਾਲਾਂਕਿ ਉਹ ਅਸਲ ਵਿੱਚ ਸੁਤੰਤਰ ਸਨ।
ਗਜਪਤ ਸਿੰਘ ਸਦਾ ਜੀਂਦ ਰਾਜ ਨਾਲ ਟਕਰਾਅ ਵਿੱਚ ਰਹੇ, ਜੋ ਫੁਲਕੀਅਨ ਰਾਜਨੀਤਿਕ ਮੁਕਾਬਲੇ ਦਾ ਹਿੱਸਾ ਸੀ।
ਇਹ ਤੱਤ “Administration of Jind State” ਥੀਸਿਸ ਵਿੱਚ ਵਾਫ਼ਰ ਮਿਲਦੇ ਹਨ। ਗਜਪਤ ਸਿੰਘ, ਉਸ ਦੇ ਸਨਮਾਨ, ਅਤੇ ਜੀਂਦ ਦੇ ਰਾਜਧਾਨੀ ਬਣਾਉਣ ਵਾਲੇ ਤਤਥਾਂ ਦੀ ਪੁਸ਼ਟੀ Jasbir Kaur ਦੀ ਥੀਸਿਸ ਕਰਦੀ ਹੈ।

Phulkian Misl
The Phulkian Misl was an eighteenth-century Sikh ruling clan, which arose in the region south of the River Sutlej. It was recognized as the twelfth misl, though it did not formally join the Dal Khalsa like the other eleven.
The lineage traces back to Phul (d. 1652), a Siddhu Jatt from the village of Mehraj (now in Bathinda district, Punjab), who received blessings from Guru Har Rai Ji, the seventh Sikh Guru, during his travels in Malwa. Phul’s house was later further blessed by Guru Gobind Singh Ji, who issued a hukamnama calling upon Phul’s descendants for military assistance, bestowing them the honor: “Tera ghar mera asai” — “Your house is my own.”
Phul had seven sons. His eldest, Tilok Singh, became the ancestor of the princely states of Nabha and Jind, while his second son, Ram Singh, was the forefather of the rulers of Patiala.
Phul’s descendants played a key role in early Sikh military campaigns, providing men and support to Banda Singh Bahadur in his battles against Mughal oppression.
Rise of Baba Ala Singh and the Foundation of Patiala
Among the prominent descendants, Baba Ala Singh, son of Ram Singh, emerged as a brave soldier and an astute politician.
By 1732, he had conquered a vast territory around Barnala, which became his headquarters. During the 1740s and 1750s, amid the Durrani-Mughal clashes in Punjab, Baba Ala Singh extended his control over many villages in the sarkar of Sirhind and occupied key towns like Sunam, Samana, Sanaur, and Tohana.
In 1753, Baba Ala Singh began constructing a fort about 100 km east of Barnala. Around this fort grew the modern city of Patiala (patti = ward; ala = of Ala Singh), which became his capital in 1763.
Baba Ala Singh died in August 1765. His grandson, Amar Singh, succeeded him and was honored with the title of Raja-i-Rajgan by the Durrani Emperor Ahmad Shah Abdali for assisting Abdali against the Marathas and other Sikh forces. However, Amar Singh’s alliance with Abdali led to the expulsion of the Phulkian Misl from the Dal Khalsa.
Amar Singh expanded the territory of Patiala significantly, acquiring lands such as Bathinda, Mansa, Kot Kapura, Saifabad, and Pinjaur, often in alliance with non-Sikh rulers.
Protection under the British
Under Maharaja Amar Singh, Patiala became the most powerful Sikh state between the Yamuna and Sutlej rivers.
In 1809, like other cis-Sutlej Sikh chiefs, his young successor Sahib Singh accepted British protection to safeguard his territory.
Patiala was subsequently ruled by:
- Maharaja Karam Singh (1813–1845)
- Maharaja Narinder Singh (1845–1862)
- Maharaja Mohinder Singh (1862–1876)
- Maharaja Rajinder Singh (1876–1900)
- Maharaja Bhupinder Singh (1900–1938)
- Maharaja Sir Yadavinder Singh, who signed the Instrument of Accession to India in 1947. Patiala was merged into the Patiala and East Punjab States Union (PEPSU) in 1948.
The State of Nabha
The Nabha branch of the Phulkian Misl was founded by Hamir Singh, a descendant of Baba Phul through his eldest son Tilok Singh. In 1755, Hamir Singh founded the town of Nabha.
In 1764, he allied with Baba Ala Singh, Sardar Nanu Singh Saini, and the Dal Khalsa in the conquest of Sirhind, receiving the parganah of Amloh as his reward.
Hamir Singh later declared independence and exercised sovereign rights, including minting his own currency. Upon his death in 1783, his son Jasvant Singh succeeded him. Jasvant Singh engaged in prolonged campaigns against Jind and Patiala to defend Nabha’s territories and successfully resisted threats like George Thomas, an Irish mercenary.
Nabha rulers also accepted British protection in 1809.
The rulers of Nabha after Hamir Singh were:
- Raja Devinder Singh (1840–1846)
- Raja Bharpur Singh (1847–1863)
- Raja Bhagwan Singh (1866–1871)
- Maharaja Hira Singh (1871–1911)
- Maharaja Ripudaman Singh (1911–1923), deposed in 1923
- Maharaja Pratap Singh, who signed the Instrument of Accession to India in 1947.
The State of Jind
The third Phulkian state, Jind, was founded by Gajpat Singh (1738–1789), the middle son of Sukhchain Singh, a descendant of Phul.
In 1764, Gajpat Singh participated in the conquest of Sirhind under Jassa Singh Ahluwalia and captured Jind, Safidon, and regions of Panipat and Karnal.
In 1766, he established Jind city as his capital. Unlike many Sikh rulers, Gajpat Singh continued to formally acknowledge the authority of the Mughal emperor in Delhi, although he was effectively independent.
Gajpat Singh often clashed with the Nabha rulers over territorial disputes, reflecting the competitive nature of Phulkian politics.

